Conference: AIAA SciTech 2024 Title: Simulations of Cryogenic Line Chilldown…
An Acoustically Adapted Synthetic Turbulence Generation Framework for Zonal Hybrid RANS/LES of Aerodynamic Flows Will Be Presented at AIAA SciTech 2023
CRAFT Tech will be presenting an acoustically adapted synthetic turbulence generation framework for zonal hybrid RANS/LES of aerodynamic flows. Balaji Muralidharan will be presenting at the 2023 AIAA SciTech Forum to be held from January 23 to January 27.
Title: An Acoustically Adapted Synthetic Turbulence Generation Framework for Zonal Hybrid RANS/LES of Aerodynamic Flows
Paper Number: https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2023-1036
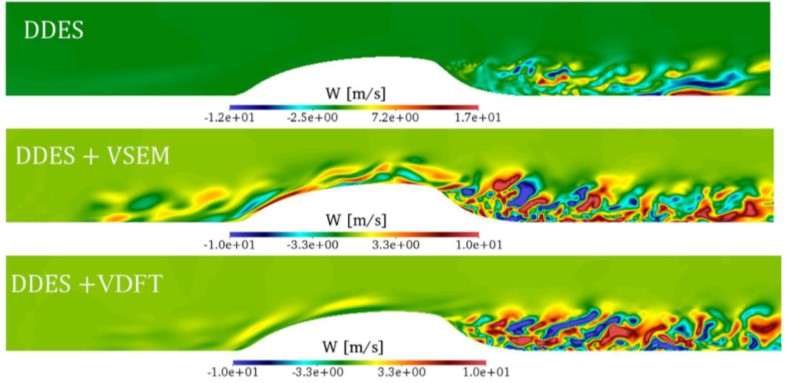
Authors: Balaji Muralidharan, Stephen M. Barr, Jonghoon Bin and Peter A. Cavallo
Abstract: This paper presents development of a generalized numerical framework for the prescription of synthetic turbulence at zonal hybrid Reynolds Averaged Navier Stokes (RANS)/ Large Eddy Simulation (LES) interfaces. The Synthetic Turbulence Generation (STG) framework developed is an integration of various existing approaches that are customized to achieve two key requirements: a) rapid transition of the artificial fluctuations into realistic and physical turbulence and b) minimization of acoustic noise generated at the interface due to injection of synthetic fluctuations. A baseline configuration of a zero-pressure gradient turbulent flow past a flat plate is used to assess multiple aspects of the various STG approaches and their extensions in detail. From the a priori study of the STG models, it was found that while the first order statistics of all the approaches converge and match with the prescribed RANS data, the higher order correlations indicate key differences. The STG models and their extensions are applied to the zero-pressure gradient flat plate case to study the behavior of the skin friction recovery and acoustic noise generation. Significant differences in the performance of the models are observed and recorded for this configuration. The customized STG framework is then applied to two complex flow configurations: flow past a two-dimensional hump and flow past a three-element airfoil. It was found that for both the cases, the addition of STG results in a better match with experimental/past data.
